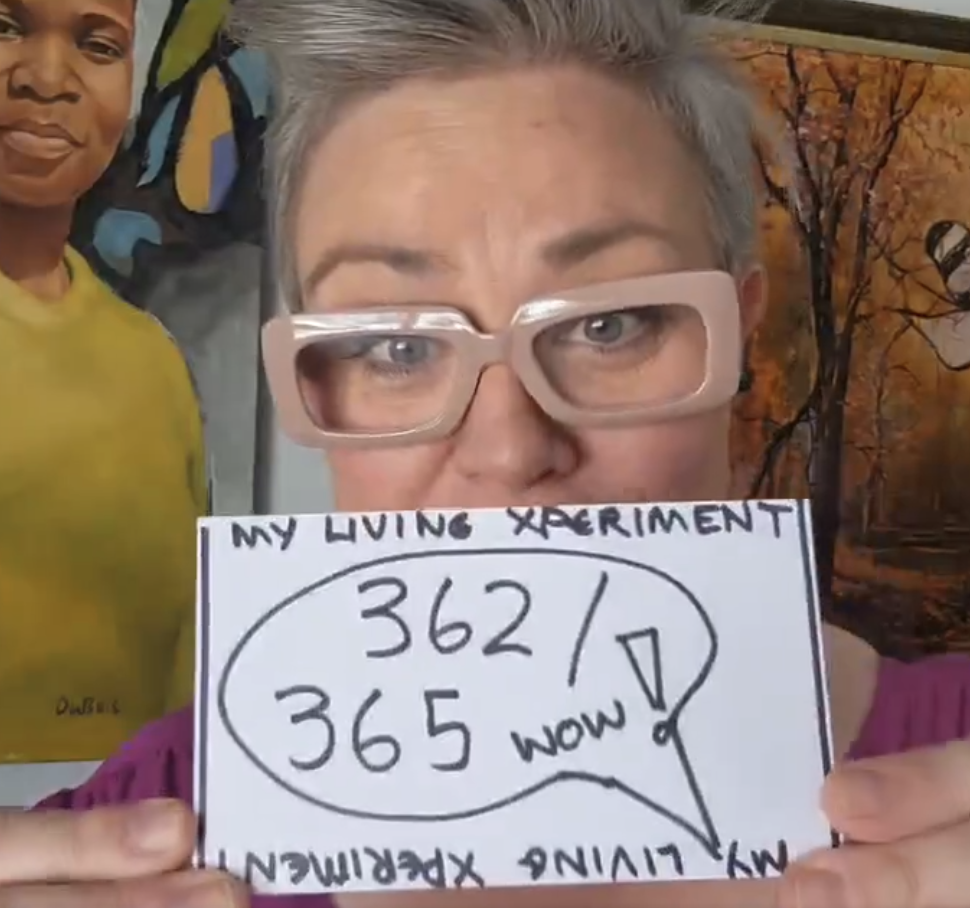PS: Methinks there’s a lesson in invoking “magic” as a joke, and then the light dimming like that at the end when I had no plan. Noted.
Video
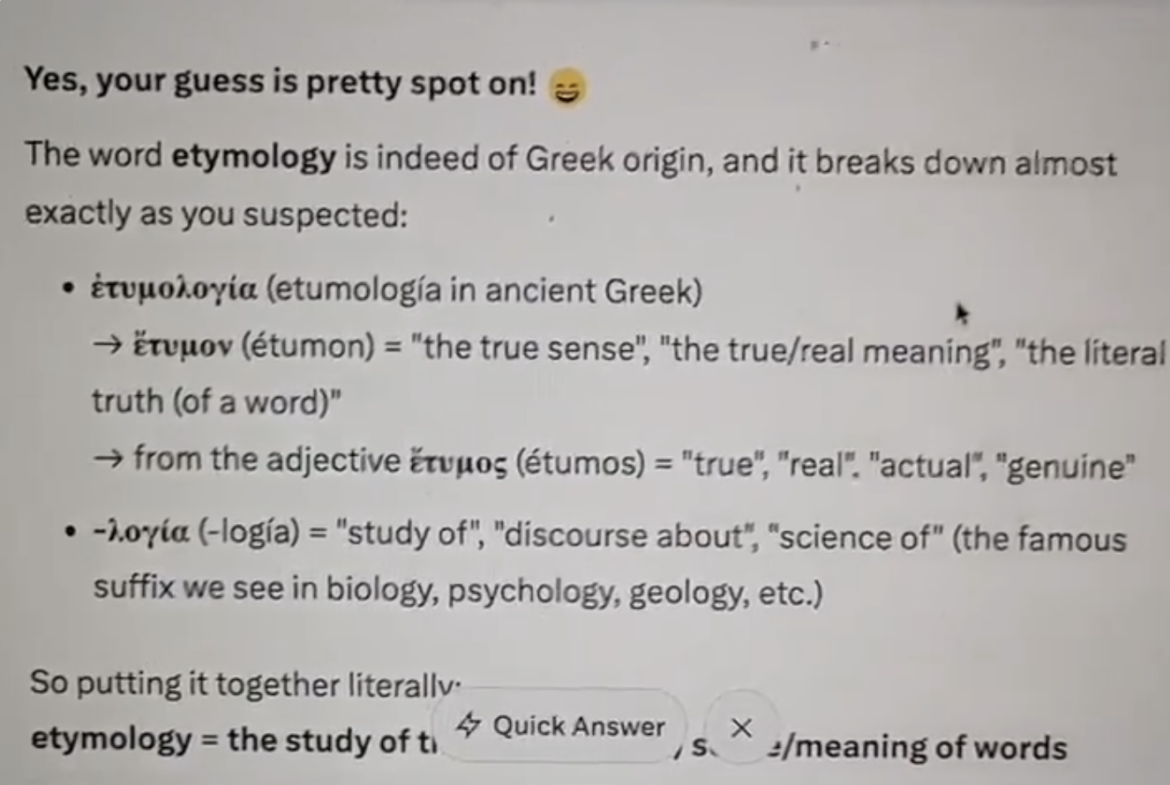
It's getting weird here towards the end of My Living Xperiment Day 363/365… I broke GROK three times today, lemme show you… https://t.co/LzXUDHaQ7w
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 29, 2025
My Living Xperiment Day 362/365: A review of COVER-UP about Sy Hersh by Laura Poitras, and wherever it takes us today… How's your Sunday shaping up? https://t.co/mek95xNSVm
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 28, 2025
My Living Xperiment Day 360/365, the Boxing Day Edition…
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 26, 2025
Eight years ago today, I quit alcohol. What I learned AKA "How to make your sloth smile." 🦥
Are YOU planning to go alcohol-free in 2026? Here are my Top 10 reasons! https://t.co/krqNLpGrnV
Merry Christmas! 🎄 Wishing you peace, love and understanding for Day 359 of My Living Xperiment ✨️ ❤️ ✌️ https://t.co/xCD7B9x6mQ
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 25, 2025
DALLE’s interpretation of “make a square graphic that represents the idea of ‘heart people’ meaning those you love and wish to spend time with”

My face when I made the heart on my chest LOL

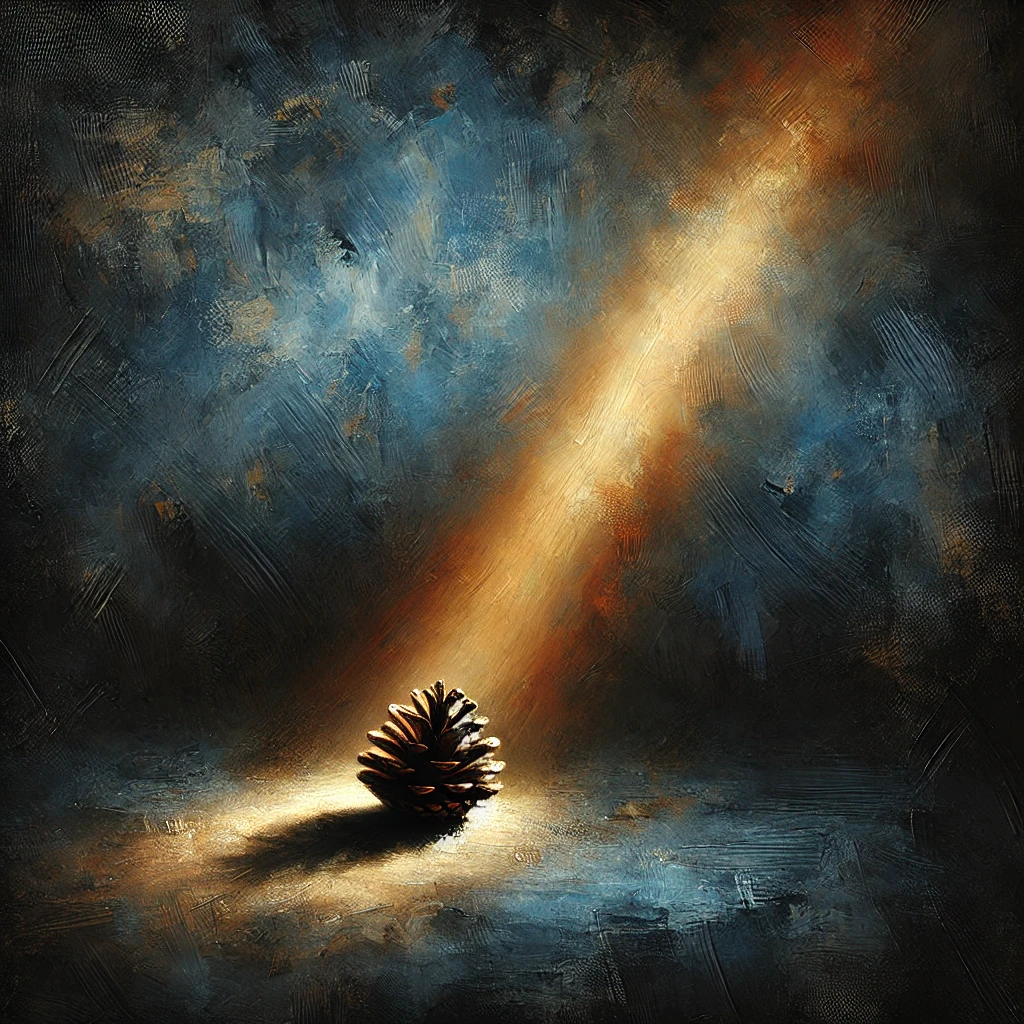
The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness has not overcome it.
— Jay Bhattacharya (@DrJBhattacharya) December 25, 2025
Merry Christmas, everyone! pic.twitter.com/LAJ2EbzTi1
Jay’s image spoke to me, so I asked DALLE to use it as a basis for a pine cone, and this is what I got…

OMG, this is another reason the @FreeStateNH is awesome! Embrace the snow! https://t.co/TuvSOx5gAv
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 24, 2025
Bonjour! Live from Quebec City one last time for Day 357 of My Living Xperiment ✨️ https://t.co/od2TtBeQ0j
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 23, 2025
Spent Day 356/365 at Strom Nordic Spa…I'm so chill, not even my hair has energy! https://t.co/g0LLchh2nU
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 22, 2025

Snowy, lazy morning in Quebec City… look at the pretty snowflakes ❄️ https://t.co/EOi280Ic7m
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 21, 2025
On top of Quebec City… Welcome to My Living Xperiment… What should I do while here? https://t.co/8ZBPx8iaW6
— Carla Gericke, Live Free And Thrive! (@CarlaGericke) December 20, 2025